Publication in the Cancers journal on the benefits of GemciTest®

Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is currently the 4th leading cause of cancer deaths, and is expected to become the 2nd cause of cancer death by 2022. For nearly 80% of patients, diagnosis occurs at an advanced, nonsurgical stage, making such patients incurable.
As already used in routine in several cancers (breast, lung), it would be advantageous to differentiate patient populations, and to choose the best treatment with the best clinical effectiveness for any given patient.
Today, there are three major chemotherapy treatments for metastatic pancreatic cancer.
Among them, Gemcitabine is still an important component in PDAC treatment and is most often used as a backbone to test new targeted therapies. Moreover, there is, to date, no routine biomarker to predict its efficacy.
Acobiom proposes to implement an innovative approach to improve personalized pancreatic cancer treatment in which biomarkers were used to help in patient differentiation.
This approach is a non-invasive blood test, GemciTest®, based on the measurement of a unique combination of 9 genes, in order to predict patient sensitivity from gemcitabine, i.e. to identify the patients who are most likely to benefit from gemcitabine-based treatment as the first approach.
This unique combination of 9 genes has been identified through a large approach based on blood-based liquid biopsy analyses, transcriptome profiling, and machine learning.
Benefits: a better overall survival for selected pancreatic cancer patients
Hence, patients with a positive test (41.6%) had a significantly longer progression free survival (PFS) (3.8 months vs. 1.9 months, p = 0.03) and a longer overall survival (OS) (14.5 months vs. 5.1, p < 0.0001), as presented in the following graph.
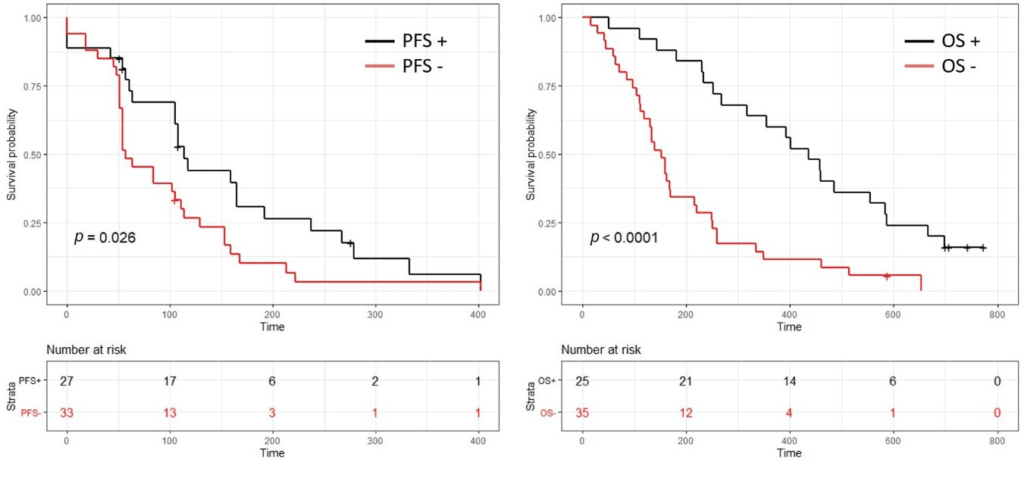
To obtain more details, please discover the scientific publication of Acobiom’s scientific team in Cancers (MDPI; Basel, Switzerland), a peer reviewed scientific journal: https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6694/12/11/3204

