Predicting patient response to the main first-line therapies in Pancreatic Cancer
Panthera DX is an innovative and non-invasive In-Vitro Diagnostic (IVD) that is capable to predict the patient response to the main first-line therapies (gemcitabine, FOLFIRINOX) used in pancreatic cancer. This IVD based on a combination of RNA markers identifies patients diagnosed with Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PDAC) who are unlikely to benefit from gemcitabine or FOLFIRINOX as first-line therapy. Panthera DX is an efficacy predictive test of the main first-line therapies used in pancreatic cancer.
Pancreatic cancer and available therapies
Pancreatic cancer is a “silent” disease that does not cause any symptom in its early stages. This disease has a poor prognosis: Most of patients will succumb to this cancer in the short or medium term (5-year survival rate = 5-10%).
According to a 2021 study by PANCAN association and researchers from Cancer Commons and MD Anderson Cancer Center, pancreatic cancer is expected to become the second leading cause of cancer deaths before 2030, surpassing the number of deaths caused by colorectal cancer. Lung cancer remains the leading cause of cancer deaths.
Today, few therapies are available in pancreatic cancer treatment.
For instance, gemcitabine, a generic drug, is used in the treatment of locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer, usually for cancers of stage 2 (SP 2) or higher.
Therapeutic combinations of gemcitabine plus erlotinib and gemcitabine plus nab-paclitaxel, received approvals based on an increase in survival, nevertheless modest compared to gemcitabine alone; i.e., median Survival (OS) gains of 0.3 and 1.8 months respectively with absolute survival gains at 1 year corresponding to 6% and 13%.
FOLFIRINOX (a combination of four drugs) is the first major advance in the management of pancreatic cancer since the overall survival and survival times without recurrence have almost doubled (Conroy T et al. N Engl J Med 2011). However, the population involved in recent clinical studies is limited to patients in “good general condition” (SP 0 or 1)1 with satisfactory liver function2, thus excluding a large number of patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer. In addition, toxicities secondary to folfirinox treatment are significant3. Thus, the safety and toxicity profile of FOLFIRINOX treatment is considered less positive than gemcitabine.
Treatments dedicated to pancreatic cancer are today based on consensus chemotherapy designed for the “average patient” without individual adaptation. However, each patient is unique, and over 70% of the time, chemotherapy is ineffective and causes harmful side effects. Thus, improving the precision and efficacy of chemotherapy to improve patient care, reduce side effects and cut associated costs has become a public health necessity.
This precision medicine approach is based on biomarkers or molecular diagnostics. It is already used in breast cancer for several years, and helps to prescribe the most appropriate, and therefore the most effective treatment for each patient.
1. In non-resectable pancreatic cancer, the choice of chemotherapy treatment is made thanks to the scales of autonomy (PS: performance status), which make it possible to evaluate the general state of the patient. The most commonly used are the Karnofsky scale and the Zubrod scale (or ECOG: Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group). The choice of treatment is completed by the data acquired during diagnosis (see §”Description of uses and modes of use”).
2. Bilirubin levels less than 1.5 times normal.
3. The grade 3-4 neutropenia rate is 45.7% vs 21% in the gemcitabine group (p<0.001) with 5.4% febrile neutropenia versus 1.2%. Moreover, the occurrence of grade 3-4 diarrhea (12.7% vs 1.8%) and grade 3 peripheral neuropathies (9% vs 0%) is much more frequent (Conroy T et al.).
Panthera DX and its medical value
Panthera DX is a significant advancement in the field of personalized medicine and the medical care management of patients suffering from Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PDAC). This real-time quantitative PCR test is capable to predict how patients will respond to the two main first-line treatments used in PDAC: FOLFIRINOX and gemcitabine-based therapies.
Scientific elements and associated medical benefits:
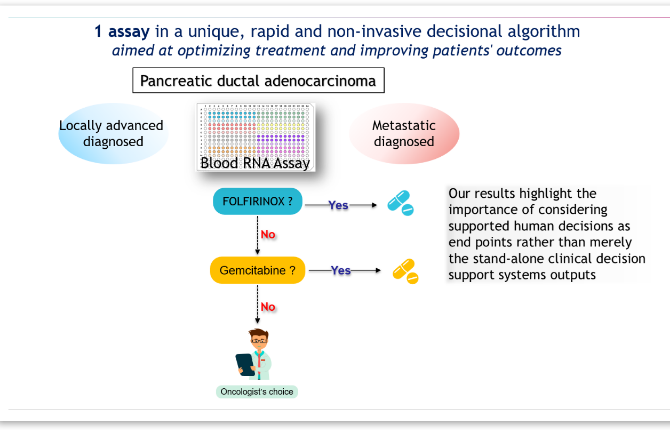
1. Therapy Guidance: Panthera DX helps determine whether a patient with metastatic or locally advanced PDAC is unlikely to benefit from to FOLFIRINOX, an aggressive treatment, or to a gemcitabine/nab-paclitaxel regimen. This ability to tailor treatment is vital since FOLFIRINOX is often more effective but can cause more severe side effects, making it unsuitable for all patients.
2. Prediction Model: The test’s predictive capability is based on two RNA signatures derived from blood samples collected from 164 PDAC patients. These signatures help differentiate PDAC patients between those who are likely to have a positive response to treatment (red curve) and those who are likely to have a negative response (black curve).
3. Patient Stratification: By using these RNA biomarkers, Panthera DX can categorize patients into subgroups based on their expected response to therapy. This stratification allows for more personalized and effective treatment strategies.
4. Prognostic Value: The test not only helps to select the most appropriate therapy treatment selection but also has a prognostic significance, as demonstrated by Kaplan-Meier plots for Progression-Free Survival (PFS) and Overall Survival (OS) in both treatment groups.
5. Clinical Validation: The model has been validated using blood samples from two retrospective clinical trials (NCT02818829, NCT03599154), reinforcing its reliability and usefulness in real-world clinical settings. These studies included patients with an average age of 68.7 years, ensuring that the test is relevant to the typical demographic affected by PDAC.
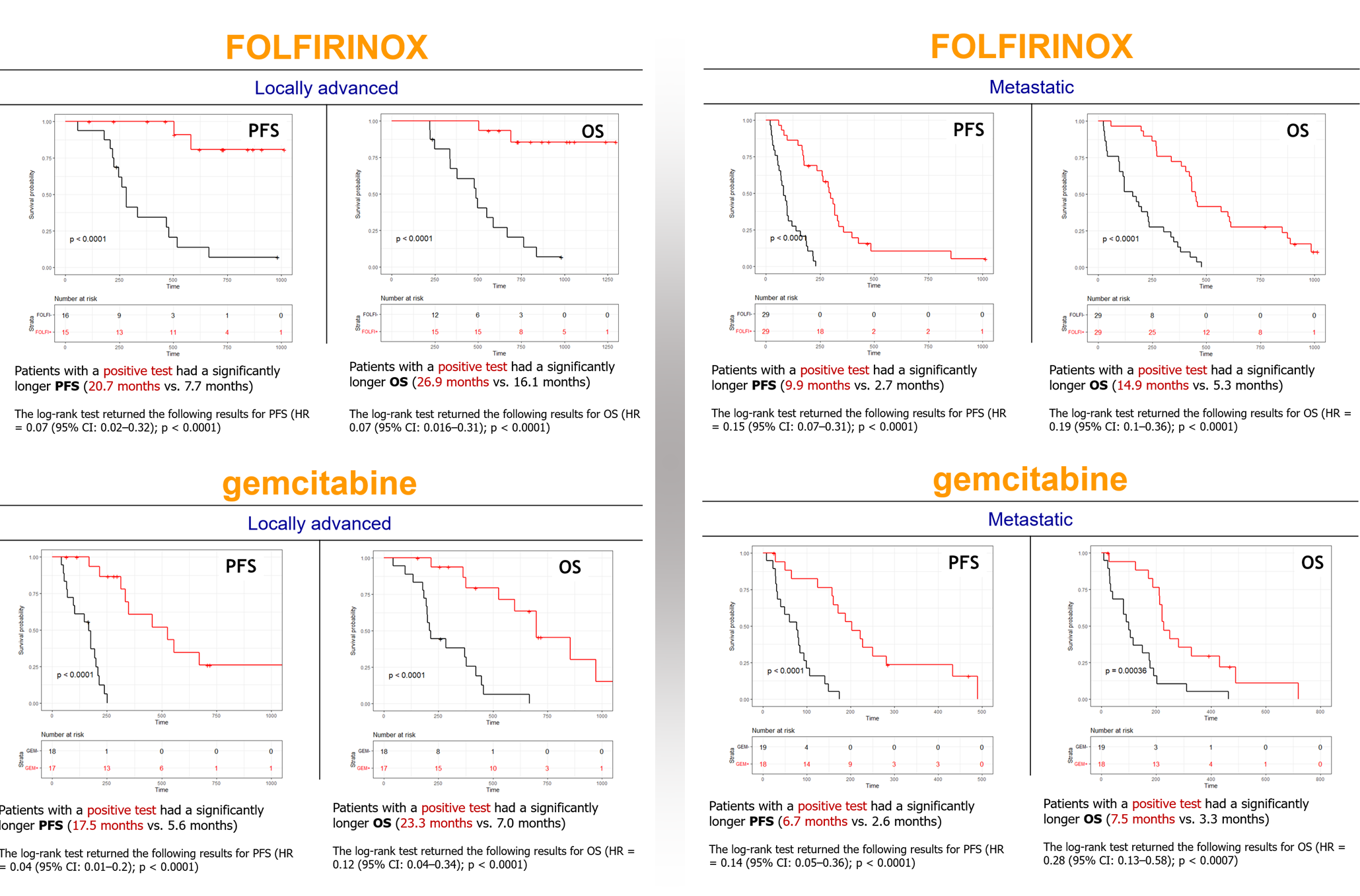
> FOLFIRINOX for locally advanced PDAC: OS = 26.9 m (positive subgroup) versus 16.1 m (negative subgroup),
> FOLFIRINOX for metastatic PDAC: OS = 14.9 m (positive subgroup) versus 5.3 m (negative subgroup),
> Gemcitabine for locally advanced PDAC: OS = 23.3 m (positive subgroup) versus 7.0 m (negative subgroup),
> Gemcitabine for metastatic PDAC: OS = 7.5 m (positive subgroup) versus 3.3 m (negative subgroup).
Key Points on Panthera DX
Panthera DX is an innovative molecular diagnostic tool that requires only a small 2.5 ml blood sample, which is collected in a PAXgene RNA Blood tube before the patient begins its first-line chemotherapy. This makes it a minimally invasive test that can easily be incorporated into a patient’s standard hospital visit.
Highlights of Panthera DX
1. Sample Collection and Ease of Use: The blood sample is collected as part of the regular pre-treatment process, requiring no additional appointments or procedures. It seamlessly fits into the standard workflow of patient care.
2. Rapid Testing with qPCR: The test uses real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR) technology to measure the expression of fourteen genes (mRNA), providing results in a few hours. This quick turnaround time enables timely decisions about treatment strategies.
3. Liquid Biopsy: Panthera DX leverages a liquid biopsy approach, which is a non-invasive alternative to traditional tissue biopsies, reducing discomfort and risk for the patient while still offering precise molecular insights.
4. Standardized Technology: The qPCR platforms used in this test are part of the Gold Standard in molecular diagnostics. They are widely employed in laboratories worldwide, ensuring the reliability and accuracy of the test results.
5. Results within 2 days: An analysis based on Panthera DX can be delivered within 48 hours, enabling quick treatment decisions and timely initiation of therapy, crucial for aggressive cancers like PDAC.
Overall, Panthera DX provides an efficient, non-invasive, and reliable method to support clinical decision-making for patients with Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PDAC), aligning with globally accepted diagnostic standards.

