Predicting Patient response to a gemcitabine-based treatment in Pancreatic Cancer
GemciTest® is an innovative and non-invasive In-Vitro Diagnostic (IVD) that is able to predict the response to a gemcitabine-based first-line treatment in patients with a form of pancreatic cancer: the metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma (mPDAC). This CE-marked IVD based on a combination of RNA markers identifies which patients diagnosed with mPDAC do not benefit clinically from a first-line gemcitabine therapy, alone or in combination. GemciTest® is a predictive test of gemcitabine efficacy.

Pancreatic Cancer and available therapies
Pancreatic cancer is a “silent” disease that does not cause any symptom in its early stages. A large number of patients have metastases at diagnosis. For them, chemotherapy remains the only therapeutic option.
This cancer has a poor prognosis: 90 to 95% of patients with pancreatic cancer will succumb to the disease in the short or medium term (5-year survival rate = 5-10%).
According to a 2021 study by PANCAN association and researchers from Cancer Commons and MD Anderson Cancer Center, pancreatic cancer is expected to become the second leading cause of cancer deaths before 2030, surpassing the number of deaths caused by colorectal cancer. Lung cancer remains the leading cause of cancer deaths.
Today, several therapies are available in pancreatic cancer treatment.
For instance, gemcitabine, a generic drug, is used in the treatment of locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer, usually for cancers of stage 2 (SP 2) or higher.
Therapeutic combination of gemcitabine plus erlotinib and gemcitabine plus nab-paclitaxel, received approvals based on an increase in survival, nevertheless modest compared to gemcitabine alone; i.e., median Survival (OS) gains of 0.3 and 1.8 months respectively with absolute survival gains at 1 year corresponding to 6% and 13%.
FOLFIRINOX (a combination of four chemotherapies) is the first major advance in the management of pancreatic cancer since the overall survival and survival times without recurrence have almost doubled (Conroy T et al. N Engl J Med 2011). However, the population studied in recent clinical studies is limited to patients in “good general condition” (SP 0 or 1)1 with satisfactory liver function2, thus excluding a large number of patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer. In addition, toxicities secondary to folfirinox treatment are important3. Thus, the safety and toxicity profile of FOLFIRINOX treatment is considered less positive than gemcitabine.
Other medical approaches are possible, such as precision medicine, based on biomarkers or molecular diagnostics. This approach, which is used in breast cancer for several years, allows for improved patient management, prescribing the most appropriate, and therefore the most effective treatment (evaluation of toxicity, resistance, etc.), and can also help to reduce healthcare costs.
1. In non-resectable pancreatic cancer, the choice of chemotherapy treatment is made thanks to the scales of autonomy (PS : performance status), which make it possible to evaluate the general state of the patient. The most commonly used are the Karnofsky scale and the Zubrod scale (or ECOG: Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group). The choice of treatment is completed by the data acquired during diagnosis (see §”Description of uses and modes of use”).
2. bilirubin levels less than 1.5 times normal
3. The grade 3-4 neutropenia rate is 45.7% vs 21% in the gemcitabine group (p<0.001) with 5.4% febrile neutropenia versus 1.2%. Moreover, the occurrence of grade 3-4 diarrhoea (12.7% vs 1.8%) and grade 3 peripheral neuropathies (9% vs 0%) is much more frequent (Conroy T et al.).
Medical interest of the Gemcitest®
Without the support of pharmacogenomic biomarkers, clinical studies show a median survival rate of 6.5 months for patients diagnosed with pancreatic cancer and treated with gemcitabine, with a 1-year survival rate of less than 20%.
In a previous clinical trial, in which patients diagnosed with pancreatic cancer (grade 3-4, non-operable, metastatic or not) were treated by gemcitabine as first-line therapy, blood samples were collected before treatment and overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) were measured.
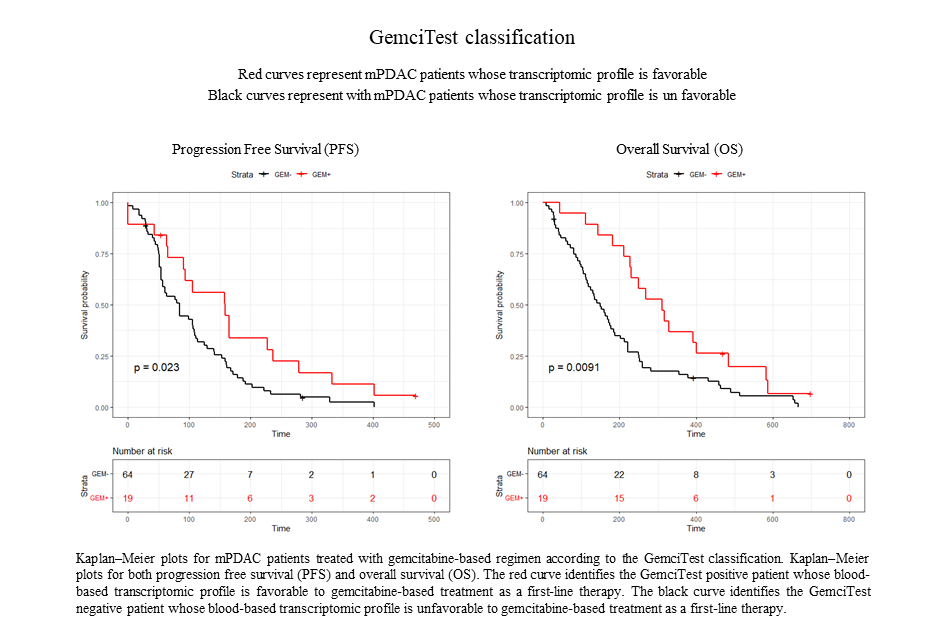
In this context, ACOBIOM analyzed the transcriptomic profiles of samples from 60 patients and selected a panel of RNA biomarkers to identify patient populations that have or have not benefited from gemcitabine-based treatment (OS superior to 8.7 months, PFS superior to 3.5 months).
Clinical validations were performed on a large cohort of 336 patients (mean age: 68.7 years; 37-88) from 2 retrospective clinical studies (including the GemciPANC trial, NCT03599154CGFL) and 2 biobanks (Carbone Cancer Center (University of Madison, Wisconsin, USA); Toulouse University Hospital (BACAP consortium, NCT02818829, France)). These cohorts included patients treated in first line with either a gemcitabine or fluoropyrimidine (5FU) based regimen.
Based on these analyses and real-world data (RWD), ACOBIOM developed the GemciTest®.

GemciTest® concerns patients diagnosed with metastatic or locally advanced pancreatic cancer and its results are obtained within one week delay.
This CE-marked In-Vitro Diagnostic is an example of the benefits of molecular tests that are able to predict patient response to treatment. It is an example of the benefits of precision medicine in the treatment of pancreatic cancer.
Analytical performance of the Gemcitest®
The analytical performance of GemciTest® (effectiveness of In Vitro Diagnostic, repeatability, inter and intra-sample variability, etc.) and its clinical performances have been confirmed (following the recommendations of the health authorities).
The results of clinical validations performed on real-world data (RWD) from patients show that those patients with clinical benefit (OS >8.7 months; PFS ≥3.5 months) identified by GemciTest® (30%) had a significantly longer progression-free survival (PFS) (5.3 months vs. 2.8 months) and a longer overall survival (OS) (10.4 months vs. 4.8 months).
A scientific article presenting these results was published in april 2023 in the revue Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology.
This study was conducted with the support of Dr. Noelle LoConte (University of Wisconsin, Carbone Cancer Center, USA), Prof. Jérôme Cros (Hôpital Beaujon, APHP, Paris, France), Prof. Barbara Bournet and Dr. Cindy Canivet (BACAP, Toulouse Hospital, France), Prof. François Ghiringhelli (GemciPANC clinical trial, CGFL, Georges-François Leclerc Center, Dijon, France), and Prof. Jean-Baptiste Bachet (Hôpital La Pitié-Salpêtrière, APHP, Paris, France).
In addition, these results were presented in a video by Dr. LoConte.
Benefits provided by the Gemcitest®
The use of GemciTest® will have important medical, societal and economic implications:
– Facilitate decision making by guiding the clinician towards the choice of optimal therapy;
– Identify the subpopulation of patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer who will benefit from gemcitabine-based therapy as first-line treatment, with a median survival of 13 months;
– Improve the quality of life of GemciTest-identified patients during their treatments (gemcitabine is one of the least toxic treatments);
– Provide a better quality of life for caregivers (gemcitabine can be administered at home);
– Control and anticipate anxiety-inducing trips to hospitals (already overloaded) and the risk of developing nosocomial diseases;
– Reduce and/or control overall healthcare costs in pancreatic cancer (gemcitabine is one of the least expensive therapies);
– Avoid the prescription of ineffective, toxic and costly therapies.
Today, health actors are facing to several major problems: the reduction of overall expenditure on health systems, the growing need to improve the effectiveness of therapies, while respecting or improving the quality of life of patients during their treatments (reduction in the time taken to treat and inequalities in this treatment between territories).
Predictive diagnostics of patient response to one of the therapies are one of the most effective solutions to meet these needs by helping physicians choose the most effective and appropriate treatment for each patient.
Using GemciTest® in combination with Gemcitabine would save costs, but more importantly would benefit patients by reducing toxicity and side effects, and improving their quality of life during therapy.

